Neurological medications
Anti-epileptic medications
Interactions between Anti-Epileptic Drugs (AEDs) and other medicines are sometimes complex, and abrupt withdrawal should be avoided as it can precipitate severe rebound seizures. These medicines should be continued pre-operatively1.
Benzodiazepines & Benzodiazepine-like
Continue these medications pre-operatively.
Examples: Alprazolam, Chlordiazepoxide, Clobazam, Clonazepam, Diazepam, Flurazepam, Loprazolam, Lorazepam, Lormetazepam, Nitrazepam, Oxazepam, Temazepam, Zolpidem, Zopiclone
Barbiturates
Continue these medications pre-operatively.
Examples: Phenobarbital, Primidone
Brivaracetam
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Carbamazepine
Continue this medication pre-operatively. Check sodium levels if bloods taken.
Eslicarbazepine
Continue this medication pre-operatively. Check sodium levels if bloods taken.
Ethosuximide
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Gabapentin/Pregabalin
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Eslicarbazepine
Continue this medication pre-operatively and check sodium levels pre-operatively.
Lacosamide
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Lamotrigine
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Levetiracetam
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Oxcarbazepine
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Perampanel
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Phenytoin
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Rufinamide
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Tiagabine
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Topiramate
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Valproate
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Vigabatrin
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Zonisamide
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Anti-Parkinsonian medications
All medicines relating to Parkinson’s disease should be continued completely as normal.
Levodopa with Dopa-Decarboxylase Inhibitor (DDI)
Continue this medication pre-operatively, including combinations. These can be taken with a sip of water until moments before induction.
Examples: Co-beneldopa: Levodopa with Benserazide, Co-careldopa: Levodopa with Carbidopa, Stalevo®: contains levodopa + carbidopa + entacapone
Catechol-O-methyltranseferase (COMT) Inhibitors
Continue these medications pre-operatively, including combinations - for tolcapone, consider checking LFTs.
Examples: Entacapone, Opicapone, Tolcapone
Monoamine-oxidase B (MAO-B) Inhibitors
Continue these medications pre-operatively.
Examples: Rasagiline, Safinamide, Selegiline
Non-Ergot Dopamine Receptor Agonists
Continue these medications pre-operatively.
Examples: Pramipexole, Ropinirole, Rotigotine
Apomorphine
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Amantadine
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Psychiatric medications
Anti-depressants
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Continue this medication as normal during the pre-operative period3. Check sodium levels pre-operatively if bloods are taken .
Examples: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Citalopram, Dapoxetine, Escitalopram, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, Sertraline
Serotonin and Noradrenaline Re-uptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Continue this medication but check sodium levels via U&E.
Examples: Duloxetine, Venlafaxine
Irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI)
Plan elective surgery with an anaesthesiologist and the patient’s psychiatrist at the earliest opportunity4. The patient should be involved in these discussions. Continuing these medications can have anaesthetic implications, and stopping them can take two weeks or more, though there is debate here. Involve specialists.
Inform anaesthesiologist if patient has taken any doses of these mnedications within two weeks of surgery.
Examples: Isocarboxazid, Phenelzine, Tranylcypromine
Tricyclic Antidepressants
Continue these medicines in the pre-operative period.
Examples: Amitriptyline, Clomipramine, Dosulepin, Doxepin, Imipramine, Lofepramine, Nortriptyline, Trimipramine
Tetracyclic Antidepressants
Continue but check sodium levels via U&E.
Examples: Mianserin, Mirtazapine
Agomelatine
Continue this medicine in the pre-operative period.
Moclobemide
Stop this medicine on the day before surgery so that 24 hours have elapsed between the last dose taken and the start of surgery.
Reboxetine
Continue this medicine in the pre-operative period.
Trazodone
Continue this medicine in the pre-operative period.
Vortioxetine
Continue but check sodium levels via U&E.
Anti-anxiety medications
Benzodiazepines & Benzodiazepine-like
Continue these medications pre-operatively.
Examples: Alprazolam, Chlordiazepoxide, Clobazam, Clonazepam, Diazepam, Flurazepam, Loprazolam, Lorazepam, Lormetazepam, Nitrazepam, Oxazepam, Temazepam, Zolpidem, Zopiclone
Anti-psychotic medications
Atypical Antipsychotics
Continue these medications pre-operatively.
If a patient taking olanzapine decides to quit smoking during the perioperative period, they should be advised to report any increase in side effects to the prescriber as dosage adjustments may be necessary. This is because tobacco is known to induce CYP1A2 resulting in reduced olanzapine plasma concentrations in smokers.
Examples: Amisulpride, Aripiprazole, Asenapine, Cariprazine, Lurasidone, Paliperidone, Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone
Clozapine
Ideally stop clozapoine 12 hours before operation to minimise the sedative and hypotensive effects without risking relapse. DO not discontinue if this proves unachievable.
Lithium
Note that in the case of Lithium, the brand name should be noted and the patient should remain on the same brand of medication at all times.
For minor procedures, continue as normal pre-operatively.
For major procedures, stop 24 hours pre-operatively5.
Check urea and electrolytes, thyroid function and ECG pre-operatively unless these have been checked within the previous 3 months.
Substance misuse
Acamprosate
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Disulfiram
Continue this medication pre-operatively.
Buprenorphine
Continue this medication pre-operatively. Leave patches in situ and send pain team referral for assistance with-operative analgesia6.
Methadone
Continue this medication pre-operatively, and send pain team referral for assistance with-operative analgesia.
Attention deficit disorder (ADD) or narcolepsy
Methylphenidate
Omit dose(s) on day of procedure.
Analgesics
Opioids
Continue these medications pre-operatively (including if used in a combination product)7. Send pain team referral if chronic opioid use/high pre-operative pain levels despite analgesic medicines.
Examples: Codeine, Dihydrocodeine, Dipipanone, Fentanyl [transdermal], Hydromorphone, Meptazinol, Morphine, Oxycodone, Pentazocine, Pethidine, Tapentadol, Tramadol
NSAIDs and COX-2 Inhibitors
Use the following procedure to determine the best recommendation for NSAID medications.
- Note bleeding risk of procedure
- Minor surgical procedures include:
- minor skin procedures (e.g. basal cell carcinoma resection)
- minor hand surgery
- cataract excision
- Any other procedures are considered high risk for bleeding. See here for further details.
- Proceed as appropriate:
LOW BLEEDING RISK
- Standard NSAIDs and COX-2 selective inhibitors: Continue8 – including combination products.
HIGH BLEEDING RISK
COX-2 selective inhibitors: Continue, (including meloxicam)
Standard NSAIDs: Except for aspirin, it may be beneficial to continue NSAID use until the day of surgery.
Recommendations: -
- Short-acting NSAID – stop 1 day before surgery, including combination products (see below).
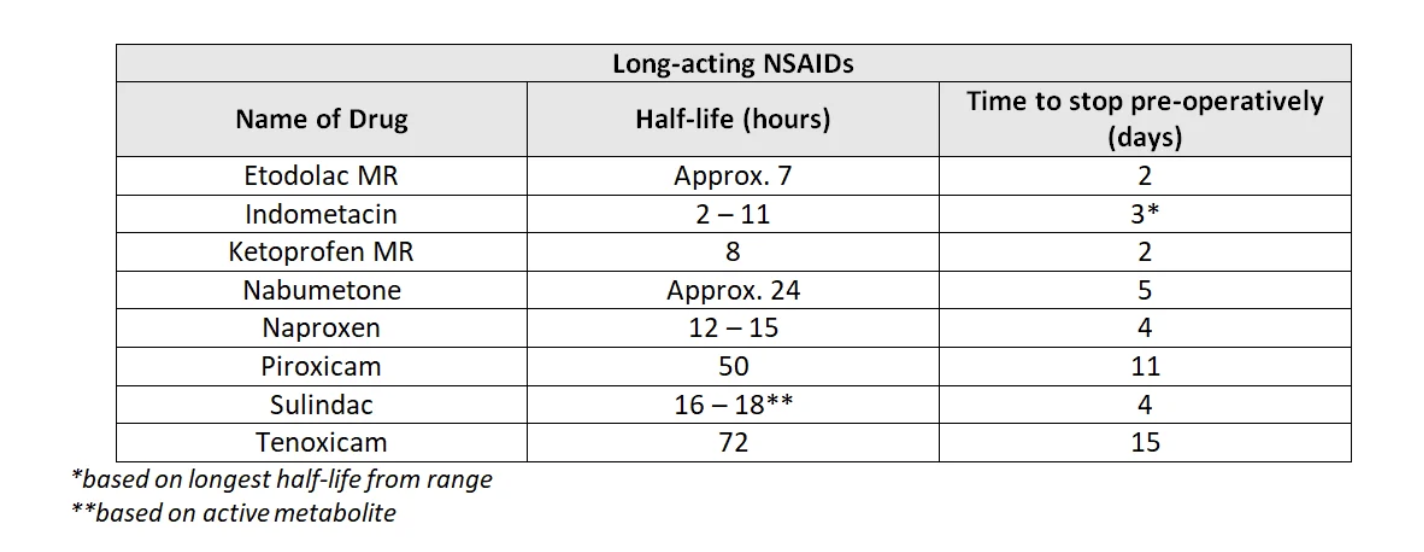
- Long-acting NSAID – stop five half-lives prior to procedure (see table), including combination products. Consideration should be given to switching to a short-acting NSAID pre-operatively if necessary and following the advice above.
- Aspirin – stop 7 days pre-operatively (including combination products) and consider using alternative analgesia.
Examples:
- Standard Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Aspirin [analgesic/high-dose > 150mg], Dexibuprofen, Dexketoprofen, Diclofenac, Etodolac, Flurbiprofen, Ibuprofen, Indometacin, Ketoprofen, Mefenamic acid, Meloxicam, Nabumetone, Naproxen, Piroxicam, Sulindac, Tenoxicam, Tiaprofenic acid, Tolfenamic acid
- COX-2 Selective Inhibitors: Celecoxib, Etoricoxib
NB: if aspirin use is for its antiplatelet activity, see section on antiplatelet agents.
Other
Methadone
Continue this medication pre-operatively, and send pain team referral for assistance with-operative analgesia.
Buprenorphine
Usually a patch, but sublingual, transdermal, and subcutaneous formulations are available. Continue this medication/patch pre-operatively9, and ensure anaesthetist made aware of patch.