ECG interpretation
Below is a guide for ECG interpretation designed for the nursing staff in the POAC. The main goal here is to identify ECGs that require review by the consultant on duty.
General
The goal is not to make particular diagnoses from the ECG, but to identify when the consultant on duty is needed to review an ECG.
Ensure any abnormality is interpreted in context for the patient:
- is there a known history of cardiac disease?
- do they get cardiac symptoms (chest pain, shortness of breath)?
- can you get any previous ECGs for comparison?
Conditions
There are several specific conditions we are particularly seeking to identify in POAC:
- Pathological brady- or tachy-cardia
- Irregularity (usually atrial fibrillation)
- Ischaemia; ST and T-wave abnormalities
- LBBB/RBBB
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Q waves signifying old myocardial infarction
- Wolf-Parkinson-White
- Long QT interval
Checklist for interpretation
If the answer is NO to any of the below questions, the ECG should be reviewed by the consultant on duty.
- Verify ECG is from correct patient and correct date
- Rate between 50-90 bpm?
- Is the rhythm regular?
- Is there a P wave before each QRS complex?
- Is the PR interval 3-5 small square (0.12-0.20s)?
- Is the QRS complex less than 3 small squares (0.12s)?
- Is the QTc between 360-440ms?
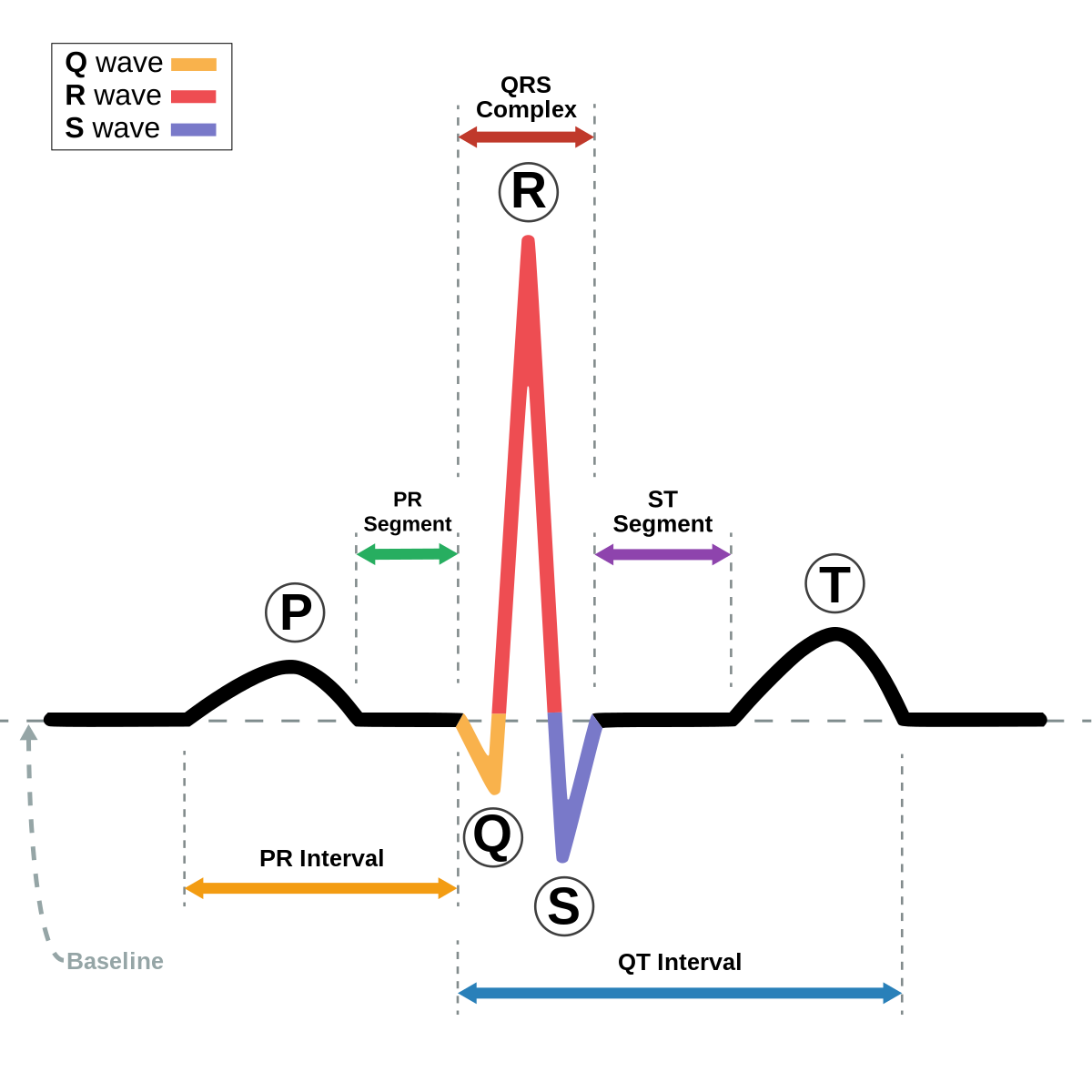
See below for clear labeling of ECG components.